Dan Freeland
04.30.2024
Answering Six Common Questions about Machine VitalsTM
1. What is Machine Vitals' primary function?
Machine Vitals is designed to monitor and analyze the health of industrial machinery, particularly those with rotating components like pumps, fans, gearboxes, and hydraulic units. It uses a set of advanced sensors to collect data on various parameters, such as pressure, temperature, and relative humidity, internally and externally. It also includes an acceleratory variance sensor and an acoustic sensor. Here’s how it functions in a nutshell:- Data Collection: Embedded within the machine, Machine Vitals gathers data from its internal and external environments using sensors placed in the oil reservoir’s headspace and on the machine’s exterior. This includes:
- Pressure, Temperature, and Humidity
- Vibration (IMU Data)
- Acoustic Signals
- Data Processing and Transmission: The device processes this data at the edge (locally on the device), summarizing critical information before sending it to the cloud every 15 minutes. This approach reduces the volume of data transferred and focuses on essential information needed for analysis.
- Analysis and Predictive Maintenance: Once the data is in the cloud, advanced algorithms analyze patterns and trends to predict potential failures or necessary maintenance activities. This proactive approach helps in preventing unexpected downtime and extending the life of the machinery.
2. What can I expect to use this data for?
- Predictive Maintenance: By monitoring trends in vibration, temperature, pressure, and other parameters, Machine Vitals can predict when parts like bearings or seals might fail. This allows maintenance to be scheduled in advance, avoiding unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime.
- Condition Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of machine conditions such as the temperature and pressure inside a gearbox or pump allows for real-time insights into the machine's operating state. This can help detect deviations from normal operating conditions, signaling the need for inspection or intervention. It serves as a watchdog in between inspections.
- Performance Optimization: Analyzing data over time helps to understand how a machine performs under various conditions. This can lead to optimizations in machine settings, adjustments in operational parameters, determining the need (or not) for ancillary products like Breathers and Filtration devices, and overall improvements in efficiency.
- Fault Diagnosis: When a machine component starts malfunctioning, the specific changes in vibration patterns, sound signatures, and other sensor readings can help pinpoint the exact nature and location of the problem, facilitating quicker repairs. The data becomes even more important in the event of a failure.
- Life Cycle Analysis: Long-term data collection helps in understanding how different components of a machine degrade over time. This can inform better design choices and maintenance schedules, and even predict the end of life for certain components, helping in budgeting and planning for replacements.
- Safety Enhancements: By monitoring critical parameters that might lead to hazardous conditions, such as overheating or excessive vibration, Machine Vitals can help in implementing safety protocols and automatic shut-down processes to prevent accidents.
- Operational Efficiency: Regular insights into machine health and performance can help optimize workflows, reduce energy consumption, and ensure that machinery is operating within the most efficient parameters.
Comparative Value: Seemingly endless comparisons can be made to evaluate what is working and what isn’t from asset to asset. You will be able to compare information from the equipment data. Be able to view comparative data from all pumps or all gearboxes, from area to area, indoor vs outdoor, different in-use oil types, in-use oil from different manufacturers, etc. You will also be able to compare equipment set-ups like Traps vs. Breathers: what works better, are breathers necessary or not in different areas, compare the functionality of different viscosities in similar set-ups, determine comparatively why one asset runs hotter than another, are some examples.
Analytical Review: It is important to have data history. In the event there is a failure, having the sensor data leading up to the failure can point to what ultimately happened and be the benchmark for what to look for in the future. That’s why there is a black box in an airplane.
Supplemental Benefits: There are some side benefits other than just the sensor data. Recording maintenance events, integrated oil analysis results, equipment run time totals and a place for all stored equipment data.
Functional Value:
- Identify data conditions of oil degradation.
- Identify data conditions related to thermal runaway.
- Identify data conditions linked to metal-to-metal contact.
- Identify data conditions susceptible to additive depletion.
- Identify data conditions susceptible to Viscosity change.
- Identify data conditions related to condensation.
- Data conditions related to water ingress contamination.
- Visualize data conditions that your equipment is expelling pressure properly.
- Identify data conditions linked to water contamination.
- Identify data conditions for equipment (seals, breathers, vents) not expelling excess pressure.
- Identify the need to add ancillary equipment such as desiccant breathers, closed system oilers, liquid level gauges, oil sampling equipment, expansion chambers, etc.
- Identify data conditions when Desiccant Breathers require replacing.
- Identify vacuum conditions related to particulate ingression.
- Identify data conditions acoustically for equipment and identify anomalies identified with poor machine condition.
- Identify data conditions indicating machine vibration for cavitation and/or alignment anomalies.
- Change your oil.
- Change your Desiccant Breather.
- Take an oil sample for further investigation.
- A physical inspection is required.
- Investigating an alert condition.
- Adding/Removing ancillary equipment like desiccant Breathers, etc..
- Schedule a maintenance event.
3. What equipment is Machine Vitals designed for?
Machine Vitals is specifically designed to monitor and analyze the health and performance of industrial equipment that incorporates rotating components and relies on oil lubrication. This includes a wide range of machinery typically found in manufacturing, processing, and utility facilities.
- Pump Systems: Including centrifugal pumps, gear pumps, and piston pumps, which are crucial in applications ranging from water treatment to chemical processing. Machine Vitals can help monitor bearing health, seal integrity, presence of water, and detect issues like cavitation or misalignment.
- Fan and Blower Systems: Used extensively in industrial ventilation, oil-lubricated bearings are found in the bearing housings that support the rotating shafts of the fans or blowers.
- Hydraulic Units: These systems are critical in many industrial applications, including presses and lifting equipment. Monitoring temperature and the presence of water can lead to action items like filtration or dry air purges before the oil is distributed to critical components.
- Gearboxes: Found in almost every industrial setting where mechanical power needs to be transferred or modified. Temperature and vibration data are key indicators of gear and bearing conditions.
- Compressors: Whether they are screw, piston, or centrifugal types, compressors are vital in many sectors. Machine Vitals can detect temperature and vibration anomalies that might indicate lubrication issues, bearing failures, or misalignment.
- Turbines: Including steam and gas turbines used for power generation. Monitoring vibration and temperature helps in maintaining blade integrity and bearing health.
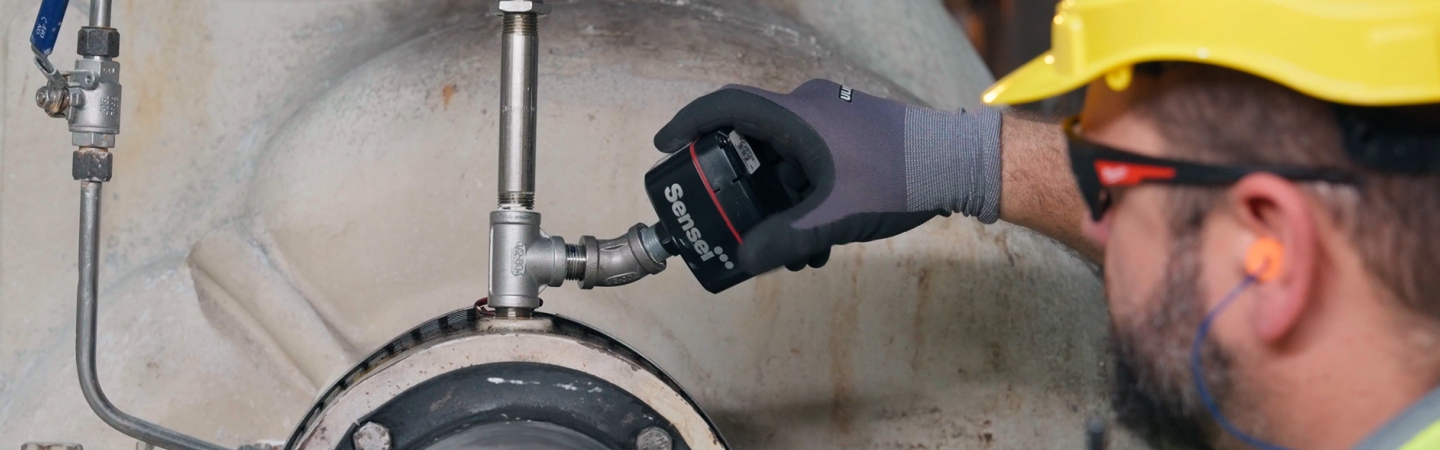
4. Where is Machine Vitals installed on equipment?
It is intended to be threaded (1/2” NPT) into the headspace of the equipment: meaning, the air space between the lubricating oil level, and the top of the equipment casing. Machine Vitals is not intended to be submerged in the oil bath, but rather above it.
5. Who is Machine Vitals intended for?
Reliability Engineers:
Here are some key benefits for reliability engineers:Improved Equipment Lifecycle Management:
- Enhanced Predictive Analytics:
- Forecast equipment performance and remaining useful life.
- This information is invaluable for long-term planning and budgeting.
- Documentation and Trend Analysis
- Historical record of equipment performance and maintenance activities.
- Trend analysis, identifying recurring issues and patterns of degradation.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:
- Informed decisions about maintenance strategies.
- Maintenance activities and resources are allocated efficiently.
- Condition-based Interventions:
- Interventions based on the actual condition of the equipment not fixed Schedules.
- Minimizes unnecessary maintenance, leading to overall cost savings.
- Proactive Maintenance Planning:
- Detect early signs of equipment degradation or impending failures.
- Identify potential issues before they escalate into critical problems.
- Reduced Unplanned Downtime:
- Address equipment issues promptly.
- Early fault detection and preventative actions
Maintenance Engineers:
Here are some key benefits for maintenance engineers:Enhanced Predictive Maintenance:
- Anticipate equipment failures before they occur, facilitating timely interventions that prevent costly downtime and extend equipment lifespan.
- Continuous monitoring and early problem detection help maintain machinery in optimal condition, enhancing overall reliability and reducing the frequency of breakdowns.
- Predictive maintenance strategies enabled by Machine Vitals reduce the need for expensive repairs and spare parts, leading to significant cost savings in maintenance budgets.
- The data collected and analyzed by Machine Vitals provides a wealth of information that maintenance engineers can use to make informed decisions. This includes identifying underperforming equipment, optimizing maintenance schedules, and improving resource allocation based on actual equipment usage and condition.
Maintenance Managers:
Here are some key benefits for maintenance managers:Cost-Effective Maintenance Strategies:
- Targeted Interventions:
- Focus resources on equipment that actually needs attention.
- Prioritize interventions based on real-time data and the actual health of the equipment.
- Minimizes unnecessary maintenance.
- Optimized Spare Parts Inventory:
- Optimize spare parts inventory. They can stock critical components based on the identified risks and potential failure.
- Strategic Planning:
- Making informed decisions about long-term maintenance strategies, equipment upgrades, or replacements
- Minimized Downtime:
- Minimizes unplanned downtime by enabling timely interventions and repairs.
- Enhanced Predictive Maintenance:
- Scheduling maintenance activities at optimal times, minimizing disruptions to operations, and maximizing equipment availability.
Maintenance Supervisor:
Here are some key benefits for maintenance supervisors:Improved Resource Management:
- Efficient Workforce Deployment:
- Optimize the deployment of maintenance personnel, directing teams to areas where interventions are needed most.
- Improving overall workforce productivity.
- Optimized Spare Parts Inventory:
- Data-driven decisions about spare parts inventory.
- Minimizes downtime associated with waiting for parts and avoids tying up capital in excessive inventory.
- Minimized Unplanned Downtime:
- Facilitates early fault detection and predictive maintenance.
- Receive timely alerts about potential issues.
- Minimizes the impact of unplanned downtime on production schedules and overall operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Equipment Reliability:
- Addressing potential issues before they lead to equipment failures.
- Prioritize preventive actions based on real-time data.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:
- Informed decisions about maintenance priorities, resource allocation, and long-term planning.
- Supports evidence-based discussions with higher management regarding equipment upgrades or replacements.
IT Professionals:
Here are some highlights for IT Professionals:Reliability & Accuracy:
- Battery Life: 2 yrs. Depending on the amount of data transferred.
- Temperature: +/- 0.1ºC
- Humidity: +/- 1%
- Pressure: +/- 0.058 PSI
- Acceleratory Variance: +/- 1%
- Acoustic: -26dB ±1dB @ 94dB SPL
- Bluetooth enabled
- Device Pairing
- Data Capture of Equipment
- Navigation Tree
- Infrastructure Status
- View/Manage Alerts by Asset
- Ethernet: 10/100 Mbps
- Wireless 2.4 GHz 802.15.4
- System Integration / API Capability
- Easy Set-up and Installation
- AES-128 Encrypted Network Joining Scheme
- Pre-Shared Key and Rotating Session Key
- AES-128 Encrypted Secure Data Transmission
Safety Coordinators:
Here are some key benefits for safety coordinators:Enhanced Worker Safety:
- Early Detection of Safety Risks:
- Identify safety risks before they escalate into hazardous situations.
- Minimize the risk of accidents and injuries related to equipment failures.
- Preventive Maintenance for Critical Components:
- Safety coordinators can ensure that critical safety-related components are consistently maintained in optimal condition.
- Contributes to a safer working environment by reducing the likelihood of equipment malfunctions that could compromise safety.
- Documentation of Maintenance Activities:
- Provides a detailed record of maintenance activities.
- Provides documentation to demonstrate compliance with safety regulations and industry standards.
- Shows a commitment to maintaining equipment in a safe and reliable condition.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making:
- Evidence-based decisions regarding the safety of equipment.
- Support claims about the effectiveness of maintenance practices and the overall safety of the industrial processes.
- Minimized Unplanned Downtime:
- Contributes to minimizing unplanned downtime.
- Reduces the risk of safety incidents associated with sudden equipment malfunctions.
6. What are some typical industries Machine Vitals can be found?
Pulp and Paper:
The pulp and paper industry relies heavily on a variety of complex machinery for its operations, making it an ideal sector for implementing Machine Vitals.Ideal Applications:
- Gearboxes: Pulpers, Presses, Dryers, Mixers, Washers, Clarifiers and Conveyors
- Pumps: Digesters, Refiners, Washers, Headbox Pumps, Press Pumps, Dryer Pumps, Clarifier Pumps, and Boiler Pumps
- Hydraulic Tanks and Storage Tanks: Hydraulic systems, Lube Room Storage Tanks, Totes, and Drums.
Water and Wastewater:
Ideal Applications:- Gearboxes: Clarifiers, Sifting Equipment, PD Pumps, Agitators, Mixers, and Decanter Centrifuges.
- Pumps: Intake Pumps, Screening Pumps, Clarifier Pumps, Aeration Tank Pumps, Filtration Pumps, Chemical and Disinfection Pumps.
- Hydraulic Tanks and Storage Tanks: Hydraulic systems, Lube Room Storage Tanks, Totes, and Drums.
Power Generation:
Ideal Applications:- Gearboxes: Cooling Tower Fans, Belt Feeders, Conveyors, Crushers, and Separators.
- Pumps: ID and FD Fans, Condensate Pumps, Circulating Water Pumps, Boiler Feed Water Pumps, Rotary Atomizers, and Turbine Lube Oil Pumps.
- Hydraulic Tanks and Storage Tanks: Hydraulic systems, Lube Room Storage Tanks, Totes, and Drums.
Extrusion and General Manufacturing:
Ideal Applications:
- Gearboxes: Extruders, Haul Off Units, Cutting and Sizing Equipment, Calendering Machines, Roll Stands, Mixers, Blenders, and Feed Systems
- Pumps: Cooling Pumps, Circulating Pumps, Hydraulic Pumps, Screen Pumps, Injection Pumps, Vacuum Pumps.
- Hydraulic Tanks and Storage Tanks: Hydraulic systems, Lube Room Storage Tanks, Totes, and Drums.